PanHunter FAQ page
About Evotec and PanHunter
What is the research focus?
- The major part of Evotec’s revenue generates from CRO-services that focus on the partnered drug discovery
- 14 different sites where the scientists are working on various projects: diabetes and its complications, inflammation and immunology, iPSC-based research and so on
- Many studies are based on high-throughput compound screening and patient materials
Which data types do we have?
- Transcriptomics > genomics = proteomics > clinical data > metabolomics
Which tools are we using in Evotec?
- We have a bioinformatics team who develop internal solutions along the needs of individual research projects and time spans
What kind of RNA-seq do we have?
- Bulk RNA-seq: deep sequencing, usually paired-end
- Single cell RNA-seq, 3’-focused
- Spacial transcriptomics, 3’-focused
- Screen-seq / Plate-seq: 384-well plate, 3’-focused
What is the advantage of screen-seq?
- Unbiased experiment for large-scale drug / compound screens (384-well plate)
- Automated robust workflow, every sample is handled with equal condition
What makes PanHunter different from other software solutions?
- PanHunter is truly multi-omics as it has means of integrating more than one omics type and supports multi-omics analysis. Compared to other software it is relatively fast and offers most comprehensive set of tools needed for omics analysis. It also comes with bioinfo support and is built in a modular way, which makes it very easy to add additional app if needed.
When is PanHunter applicable?
- When having omics data (transcriptomics, proteomics, genomics, metabolomics…)
- When obtaining big and complex data that can be converted to count matrices (phenotypic readout, cell painting, flow cytometry…)
- When robust pipeline and algorithms are required
- When collaborative work space is beneficial
When is PanHunter not applicable?
- When the scientists only perform simple bioassays such as western-blot, qPCR, ELISA, fluorescence read-out from a couple of antibodies or reagents etc.
- When experiment protocol (e.g. cell differentiation protocol) is short: only few steps and very time-efficient. In this case, conducting omics studies (~3 weeks to obtain transcriptomics data) would be too long and expensive, and it’s not possible to keep some cells viable for so long.
How can PanHunter help in Phase I, II, III of clinical studies?
- Patient Data app is especially useful for post experiment stratification.
What is the source of the algorithms? Where to find the information?
- Mixture of peer reviewed, internal development and external sources.
- The information is available in PanHunter documentation, which can be accessed by clicking on the Help button in PanHunter.
Are there any PanHunter tools which recognize picture and text?
- No, there are no tools which can be used for text and picture data mining.
PanHunter Access
How do I start PanHunter?
PanHunter is a web-based analysis platform that runs on Evotec servers. The users can open one of the below URLs with a modern web browser of choice, to log in and start PanHunter.
What should be used as login credentials?
- The username and the password are the same as the Microsoft Windows ones.
- In case you are not based in Germany and/or cannot find your PanHunter projects after logging in, please try to log in with username@corp instead of your Windows username alone.
Which browser should be used to access PanHunter?
- Google Chrome is recommended; nevertheless Mozilla Firefox and Microsoft Edge should work just fine.
- If you have any problems accessing PanHunter via a stably working VPN, please try to use an incognito window.
Can multiple users use PanHunter at the same time?
- Yes, PanHunter supports collaborative access. It makes sure one does not overwrite other people’s inputs; everything is saved on the fly in a dedicated secure environment.
Where to see different PanHunter projects and studies?
- All accessible PanHunter projects of the user are shown as separate tabs at the top of the Start page.
- Within a specific PanHunter project, users can find its related studies and access them via the included available apps.
How to request access to PanHunter projects?
- Please send the request to panhunter_support@evotec.com, include the project lead in cc and provide the following information:
- Windows username of the user
- Name of the PanHunter project
How to request creating a new PanHunter project? Which information is required?
- Requests can be handed in through SharePoint EvoFlow, Admin app or email to panhunter_support@evotec.com
- Required information:
- Project name: desired name to be displayed in PanHunter
- Project ID: internal unique identifier of the project, only lower-case letters and/or numbers
- Species
- Name of the project lead(s)
- Project billing code, i.e. IFS code
- Optional: short description of the project
Data Integration and Export
Which data formats can be integrated into PanHunter? Is it possible to integrate other data types?
- For transcriptomics datasets, PanHunter accepts and prefers fastq files generated directly from sequencing machines.
- For other omics types or assays such as proteomics, metabolomics, phenotypic readouts, cell painting, etc., count matrices, bam files, R- and python-generated files can be integrated smoothly.
Is it possible to integrate and evaluate 120k Genomics?
- Yes, PanHunter can support it. Human genome contains approximately 120,000 genes.
Is it possible to integrate experimental metadata?
- Yes, it is supported.
Which species are applicable in PanHunter?
Organisms listed below are fully supported. Integration of other species or customed metadata is possible; discussions on the requirements at an early stage is needed.
- Human (Homo sapiens/Hs)
- Rat (Rattus norvegicus/Rn)
- Mouse (Mus musculus/Mm)
- Macaques (Macaca mulatta/Mmul, Macaca fascicularis/Mf)
- Pig (Sus scrofa/Ss)
- Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus/Cgri)
- Dog (Canis lupus familiaris/Cluf)
How long does it take to integrate a new study?
- It depends primarily on the provided data; fast and robust procedure has been established for fastq files. Other data types can be integrated within a workweek.
Where to find the date of study integration in PanHunter?
- This feature is under development. At the moment, it is not visible via the graphical user interface.
Is it possible to provide raw data files for the users?
Yes, fastq, bam and count matrices can be provided. However, files that are generated during pre-processing (e.g., demultiplexing) are usually discarded due to the fact that they are uninformative and space-intensive.
Following data files can be exported directly from the New Comparisons app in PanHunter:
- Transcriptomcis data:
- raw: raw counts per gene
- norm: count per million (CPM)
- lognorm: log2 of the CPM values
- For ScreenSeq data:
The formula for calculating log-normalization of ScreenSeq data is $log2(CPM/100 + 1)$. CPM is divided by 100 to adapt to initially (now substantially improved) shallow gene counts where counts per 10K count unit was more applicable. A pseudocount is added to avoid 0 count that is not accepted by log function.
- Proteomics data:
- norm: normalized protein intensities
- lognorm: log2 of normalized protein intensities
Can data be exported, modified and reintegrated into PanHunter?
- It is feasible, however not via the graphical user interface yet. Please contact us through the Contact Support button or panhunter_support@evotec.com.
Sample Selection
How to select samples to be analyzed?
Selecting samples is performed as follows:
- In the left panel, there is a Sample selection menu. By default, it is empty and the user needs to select a study first.
- To select a study, please click on the empty Values field in Filter: Study section and choose at least one study from the drop down menu.
- Additional specifications can be defined by selecting different modifiers from the drop down menu at the bottom of the Sample selection. Available modifiers are Filter categ., Filter num., Join Columns, Column binning and Enrich .
- After selecting the desired modifier and clicking on +, new sections should appear accordingly.
- For detailed explanations, please check out the tutorial video: How to use the New Sample Selector?
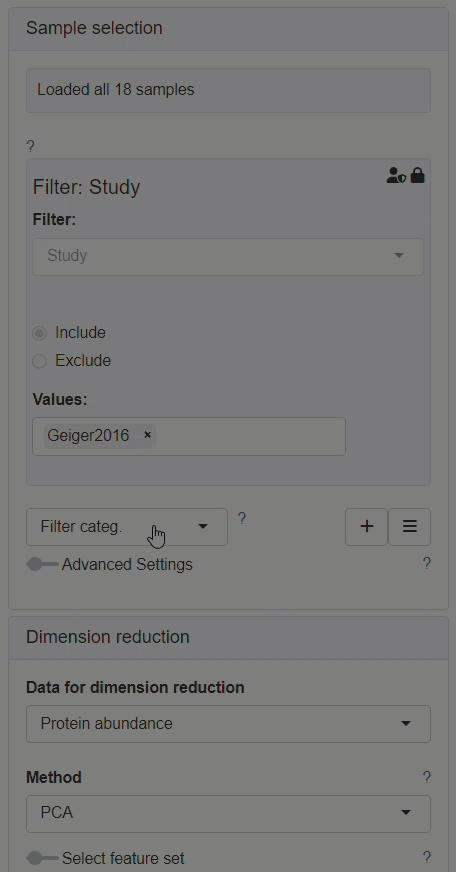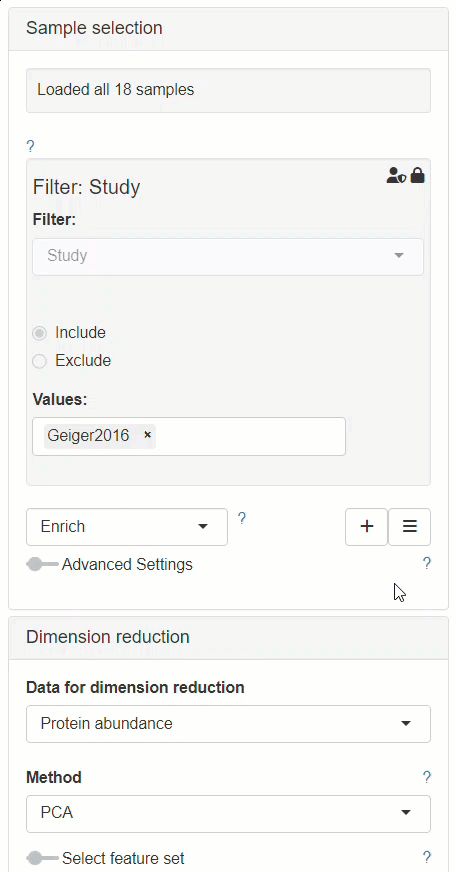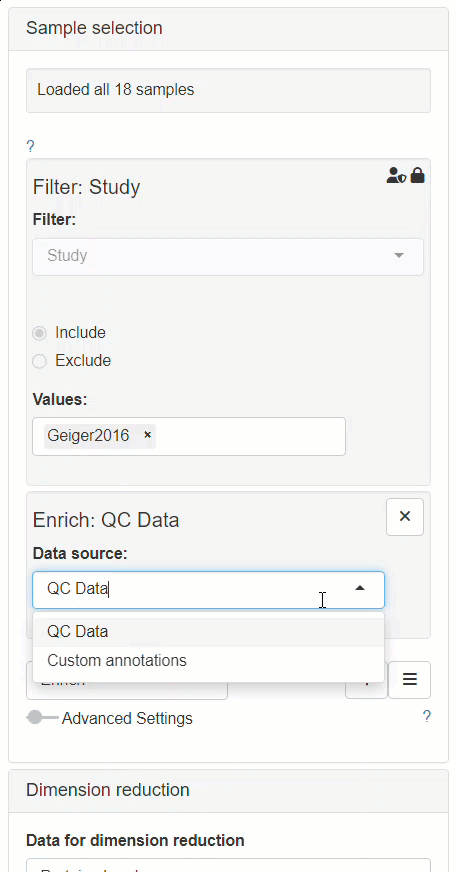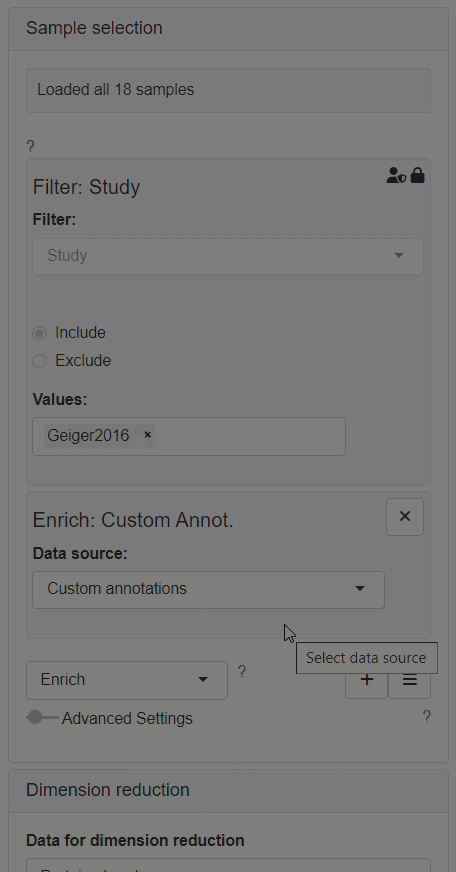
How to enable custom annotations in the New Comparison App?
Enabling custom annotations is performed as follows:
- The modifier Enrich needs to be added to the Sample selection menu.
- After Enrich section has appeared, Custom annotations should be selected as the data source for the enrichment.
- The Sample annotations section should be available for editing afterwards, in the left panel.
How to select samples in a dot plot?
Samples dots can be selected via:
- Lasso tool: by clicking and holding the right mouse button, and circling the samples of interest
- Figure legend: by clicking on the legend item, the samples in the corresponding category will be selected
The users can combine multiple selections by holding the shift key while selecting them. Holding the ctrl key, on the other hand, can deselect the samples.
Sample QC
Which omics data is applicable to check it with the Sample QC app?
- Transcriptomics data; bulk RNA-seq, single-cell RNA-seq and plate RNA-seq/ScreenSeq are applicable.
- For proteomics data, please use the Proteomics QC app.
What is a good indication of a qualified sample?
- With advanced technology nowadays, >80 % uniquely mapped reads can be obtained from a sample with good quality. Additionally, >90% demultiplexed reads can be achieved by ScreenSeq. However the definition of a good sample strongly depends on the experimental setup (e.g. model organism or a cell line).
- The mentioned two indicators: uniquely.mapped.reads.percent and PercentDemux, can be found in the Alignment stats and in the Files subtab of plateRNA-Seq, respectively.
Why low quality samples need to be removed and what happens if they are kept?
- Low quality does not come without a reason and we never cannot exclude that the same reason would affect the gene expression profile. Moreover, low quality typically leads to an effectivly shallow quantification of gene expression, which leverages the contribution of noise.
- If the low quality samples are kept, it may (and most probably will) affect the interpretation of gene expression quantification and differential expression analysis.
How to get an overview of the behaviors from all barcodes in the plate of a ScreenSeq dataset?
- During plate RNA-seq, each well of the plate is labeled with a specific barcode. To check the behavior of the barcodes, a visual overview is provided in the Plate/Library subtab in the plateRNA-Seq section. Detailed information of selected barcodes can be inspected in the Barcode Corrections subtab.
What is barcode bias?
- Barcode bias describes the fact that some barcodes generate less reads, i.e. lower sequencing and demultiplexing efficiencies, than others due to its own nature. Nevertheless, all reads are corrected at the end in PanHunter.
What is barcode correction?
- When one mismatch occurs during synthesis or sequencing, it’s automatically corrected at the barcode correction step during data pre-processing.
Do genes that show zero count be filtered out during pre-processing?
- Yes, only the detected genes are shown in PanHunter.
Does Sample QC app allow the users to remove outliers?
- Outliers are usually flagged by our application experts already while performing the raw data QC during data integration. They are excluded since they can negatively influence the analysis results.
- If desired, the users can display and include the excluded samples in analyses through the PanHunter graphical interface, by activating the Advanced Settings via the slider and selecting Show excluded samples in Sample selection section.
Comparisons
Comparisons between different data sources
Is it possible to compare different layers of omics data?
- Yes, depending on the research question, one can compare between different samples, studies, omics types, and even different species.
How to compare studies from different projects?
- Please contact PanHunter support (panhunter_support@evotec.com) for transferring selected studies to desired projects or combining projects.
Is there a way to compare different omics results?
Yes, multiple apps in PanHunter support side-by-side comparison and analysis between top tables calculated with different omics types.
- Top Tables: Results of up to 4 top tables can be compared side-by-side in the Compare Top Tables tab.
- Cross-Comparison: Samples from different datasets can be linked and visualized in dimension reduction plots.
- MA Plot: Top Tables calculated using different datasets can be visualized in volcano plots.
- Pathway Mapping: Top Tables calculated using different datasets can be visualized on pathway schemes.
Is it possible to correlate omics data with clinical data?
- Yes, Patient Data app is dedicated for exploring clinical data and correlating it with omics results. It´s also possible to enrich patient data information via the Enrich modifier in Sample selection and use it in other apps. Please see Sample Selection for more details.
New Comparison app
What is a PCA plot and how to read it?
- A PCA plot, or a Principal Component Analysis plot, is a dimension reduction plot where samples are clustered together based on their similarity while preserving the maximum amount of information. PCA Component 1 and PCA Component 2 are displayed on plot axes automatically as components with highest cluster forming significance. That is, the closer the sample dots cluster together in a PCA plot, the similar their transcriptome/proteome profiles are.
- In PanHunter, PCA plot is accompanied by additional bar plot where all PCA Components are displayed with corresponding standard deviation.
Is it possible to change the number of components used in generating a PCA plot?
-It´s possible to select the number of total principal components to be calculated by enabling Set additional parameters and then Set number of PCs in Dimension Reduction section in the left panel. To display other calculated principal components on plot besides PC1 and PC2, please enable Select Principal Components via the slider.
Why does the PCA in PanHunter look different to the one I have created manually?
Behind the scenes, a series of steps are done before the samples are plotted in PCA space.
- By default, only the top 500 features with the most variance are included in the dataset.
- Data are loaded from the matrices with the respective main datatype given its platform.
- NA values are mean imputed
- Values are centered but not scaled
- The calculation is done with done either with irlba::prcomp_irlba or, if this fails, with stats::prcomp
Minor numerical differences can lead to the inversion of Principal Component (PC) transformed values. As a result, visualizations of the data may appear mirrored along the respective axis of the transformed dimension. However, this does not affect the overall interpretation of PCA results.
Which algorithm is applied on the Exploratory analysis?
- Algorithm based on which samples are clustered calculates pairwise distances. We use Mann-Whitney U test on intra- and inter-class distances (for categorical) and Spearman‘s rank correlations between pairwise distances and differences of a variable (for numerical).
What does “coverage” of a Comparison Group mean in dimensionality reduction?
- When choosing Comparison analysis as the Data for dimension reduction, a coverage in % will be provided together with the available Comparison Groups. It is the proportion of comparisons by the number of SampleIDs in the Study.
- For example, if there are 4 compounds and 1 control, each having the same number of samples, the coverage will be 4/5 = 80%.
What can be used to specify the formula when creating new comparisons?
- The categorical and numerical variables in the sample metadata as well as saved custom annotations can be used to specify the comparison parameters for running differential analysis in the New Comparison app.
- In case of confounding/batch effects, it is recommended to include associated covariates in the model, if it keeps model complexity reasonable for model fitting. For example, PlateID is included as covariate for ScreenSeq data.
How to decide which statistical method should be used when creating new comparisons?
Two statistical methods are available in PanHunter:
- DESeq2: the method is optimal for data containing discrete numbers, e.g. count values from transcriptomics data sets.
- Limma: the method is optimal for data containing continuous numbers such as feature intensities from proteomics and metabolomics data sets.
By default, the optimal statistical method will be automatically selected by PanHunter. Nevertheless, if desire, another method can be selected manually.
Why does PanHutner switch to use Limma when >100 samples are included when creating new comparisons, even for transcriptomics data?
- Limma is less compute intensive and can generate results faster for larger studies. Nevertheless, users can apply DESeq2 manually if needed.
When Limma is used, is Voom precision weights included in the models?
- Yes, if we perform differential expression analysis with Limma for RNA-Seq data, Voom precision coefficients are applied.
For ScreenSeq data, why is it recommended to use DESeq2 instead of Limma/Limma-Voom despite the high sample numbers?
- Indeed ScreenSeq studies usually have >100 samples, however, DESeq2 is recommended especially when one of the groups in a comparison contains a small number of samples. The suggestion is based on our internal benchmarking studies as well as the fact that the statistical model used in DESeq2, negative binomial distribution, is more consistent in comparison with the “continuous” statistical model used in Limma. Consistency needs to be considered as there is a limited sequencing depth in ScreenSeq for individual samples, counts for genes are pronouncedly discrete, especially for lower expressed one.
MA Plot
Is it possible to show only one top table in MA Plot app?
- Currently there is no option to see the MA/Volcano plot only for one previously saved top table. Our developers are aware of this and are working on a solution. It is possible, however, to select the same top table in both entries in the MA Plot app. In this case, both the correlation plots between log2 fold change and between abundance of the two datasets should display perfect matches as the input top tables are identical.
Drill Down
How to compare the expression of one gene across different cancer types?
- Gene Info app is dedicated for checking the expression values of a single gene across different conditions. Please specify the search parameters first, such as the studies of interest (i.e. cancer types in this case) and the target gene or feature, then the results will be present in a tabular or graphic view, in the Results or Graphic tab, respectively.
Is it possible to display different information in a table?
- Yes, all tables in PanHunter can be customized. Users can add and remove any column via the table setting shown as a three-bar icon located on the upper left corner of a table.
Downstream Analyses
Pathway Mapping app
Are pathways updated?
- Yes, they are updated regularly.
Can you create your own pathway?
- No, currently it´s not allowed to create your own pathways as this could result in various problems when operating PanHunter. Current available pathways are from Wikipathways.
Can you visualize different omics results on the same pathway simultaneously?
- Yes, visualizing fold changes from two top tables calculated from different omics types on the same pathway is possible, as long as the data are stored in the same project. Transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics data can be applied here (although the coverage of the mapped metabolites is low due to the fact that there is no comprehensive metabolite database yet).
Signature Visualization app
What kind of readout comes from the Signature Visualization app?
- The Signature Visualization app provides an interactive visualization of a signature against the top table genes. The bar represents genes from the selected top table: down-regulated gene in orange and up-regulated genes in blue; ordered according to the fold-change. The dots above the bar represent the signature genes; their locations correspond to the ordered top table genes in the bar and their colors reflect to the gene regulation of the signature.
Enrichment Visualization app
How are the gene set clusters calculated in the 2D plot?
- Different gene sets are compared accoding to the Jaccard index. Similar terms obtained from selected databases (ChIP Atlas, GO, MSigDB and Wikipathways) are clustered and visualized in the 2D plot.
Are all features of a gene set shown when comparing Comparison groups? Is there a way to only show the proportion of significantly regulated genes of a gene set?
- All genes that are associated with the respective gene set are shown, as long as no additional filtering is applied.
- There is currently not possible to only show the significantly regulated ones within PanHunter. When displaying FDRs of GO terms, this method is used for testing and Fisher/Wilcoxon/KS are used for Wikipathways. However there is currently no method to subset to GO terms or wikipathways of interest.
Single-Cell Transcriptomics
About single-cell technology
How many cells and reads are adequate for a single-cell transcriptomics study?
- Single-cell RNA-seq requires at least 50,000 cells (1 million is recommended) as an input; 500 to 10,000 cells per sample should be analyzed; 100,000 reads per cell is ideal to maximize the identification of transcripts.
What can go wrong during scRNA-seq?
- Commonly, microdroplet-based methods are applied during single-cell RNA-seq; i.e. individual cells are encapsulated in a microdroplet, where the reverse transcription reaction takes place, converting RNAs to cDNAs. Ideally, each droplet should contain only one cell; however, there are situations which no or multiple cells are present in one droplet.
- When a droplet does not contain a cell, only the ambient RNAs are sequenced which produces background noise. When a droplet contains more than one cell, called multiplet, high number of expressed genes in comparison to the average level would be detected. This can be identified and corrected during pre-processing and data integration.
- Moreover, a droplet can contain one or multiple dying cells. In this case, high numbers of mitochondrial transcripts will be detected. One should note that the expression level of mitochondrial genes depends highly on the tissue of interest. For instance, muscle, heart, liver, kidney, and to a certain extent, brain tissues are considered as mitochondria-rich tissues.
What is CITE-seq?
- The full name of CITE-seq is Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing. It is a method to perform single cell transcriptomics along with gaining quantitative and qualitative information of surface protein markers using available antibodies.
What is the difference between barcode and unique molecular identifier (UMI)?
- One barcode corresponds to one cell; namely, one barcode comes from one cell and one cell is labeled with one barcode (in best case, when no multiplet present). However, one UMI corresponds to one transcript; namely, one UMI comes from one transcript generated by a cell but one cell contains multiple transcripts and therefore is labeled by multiple UMIs.
- Technically, UMIs are added before PCR amplification in order to reduce errors and quantitative bias introduced during the amplification. A length of 16 nt barcode and 10 nt UMI are commonly used in the 10x genomics workflow for scRNA-seq.
scRNA-Seq Browser app
Is manual cell annotation possible?
- Yes, PanHunter provides both predicted classification based on curated database and the possibility to annatate the cells manually.
Is it possible to generate sub-clusters of selected cells?
- Yes, it is possible to generate sub-clusters using the scRNA-Seq Browser. Please select the cells of interest by holding the right mouse button and circling the target cells in the Overview tab. This will save its coordinates automatically and can be further re-calculated, visualized and inspected in the Sub-clustering tab.
Is it possible to perform trajectory analysis (pseudo-time analysis)?
- Yes, pseudotime analysis (we currently use Slingshot) can be done by in the Pseudotime tab. All lineages are available in the resulting dropdown menu and two lineages can be selected to visualize side-by-side. Differential expression calculation on top of pseudotime lineages can be also calculated.
Data Servers
How to transfer large data files with external clients?
- Uploading the data files to client’s cloud-based storage is preferred. We are well-expericenced with AWS S3 buckets and sftp.
- In case a storage bucket is not available, we can set up sftp server on our end to transfer the data. Other solutions need to be discussed.
Is it possible to store the data on client’s external server and work on them in PanHunter?
- It is possible, however requires highly complicated process. Case-by-case negotiations at business and legal levels between Evotec and the client are required.
Integrated Databases
What are the available databases in PanHunter?
- The number of integrated databases in PanHunter has been increasing; below are some examples of the integrated ones:
Gene Ontology, WikiPathways, ChIP-Atlas, UniProt, Pfam, Creeds, The human protein atlas, Protein data bank, OMIM, ChEMBL, DrugMAtrix, MSigDB, BioGRID, ConnectivityMap, e!Ensembl, TARGET, GTExPortal, NCBI, NIH
Is KEGG pathways database included?
- No, KEGG is not included. It is a commercial database which the licencing contracts and the pathway updates are difficult to navigate.
Is CMAP databses included in PanHunter?
- Yes, ConnectivityMap (CMAP) signatures are included in PanHunter. The user can use them, e.g., in the Signature Visualization app to compare a Top Table of interest against the signatures from CMAP database.
Which chemical information is used in the Chem Info app, public or Evotec´s compound collections?
- The Chem Info app is dedicated to omics compounds studies. The chemical information are part of this study. It can be either publicly available compounds or Evotec compounds.
Which publicly available data sets are integrated into PanHunter?
- More than 80 publicly available data sets including transcriptomics, proteomics, single cell and clinical data are included in following projects: TCGA, Public Cell Atlas, Rat Body Map, Cancer Cell Atlas, ScreenSeq Demo and Proteomics Demo. These projects can be openly accessible.
Are patient and genotype databases available, e.g. Estonia Biobank, DNANexus and Evotec’s proprietary databases?
- Publicly available data sets from TCGA, Human Cell Atlas etc. are accessible for every user. Additional public knowledge can be integrated by request.
- Evotec molecular patient database (E.MPD) includes molecular and clinical data of several disease areas from different patient cohorts. Access to the proprietary databases needs to be discussed.
Bug Reporting
What to do when one of the apps is crashing or not working as expected?
As a first approach, you can try to reset the user settings (see below) of the app that is causing problems. If this does not help, or if the same problem shows up repeatedly, please reach out to the PanHunter support in one of the following ways:
- Through Contact support button - fill in the form and provide all the details
- Email to the panhunter_support@evotec.com with a description of your problem, the name of the app that is not working, and the project you are using. If possible, add a snapshot link (created by clicking on “Snapshot” in the upper-right corner on your screen) or a screenshot to the e-mail and steps to reproduce the error.
How do I reset my user settings?
- Resetting user setting for an app is always a good idea if you are stuck within one app.
- To do this, there are two options:
- Hover the mouse over an app and click on the little gear icon showing on its upper-right corner. This will open up an app-specific configuration pop-up. Here, you can click the “Reset user settings” button to reset the settings for the selected app.
- If there is an “Admin” link in the lower right corner of the PanHunter start page, click it to enter the Admin page. Here, go to the “User settings” tab, select the app for which you would like to reset your settings, and press “Reset user settings”. Now, when restarting the app, you should see a clean interface. CAUTION: Please note that resetting your user settings will deselect all samples and remove all parameter values in that app. This might be undesirable and thus you should try this fix only if you are aware of the consequences.
My “Contact Support” button doesn’t work. How can I resolve it?
- Please check if Outlook has been set as the default app for email in your Windows settings. If not, go to the Windows Settings -> Apps -> Default Apps and choose Outlook as the default app for the E-mail
- If setting Outlook as the default app doesn’t resolve the problem, please contact us via panhunter_support@evotec.com
Training and Support
Here you find an overview of available training and knowledge resources.
How can I learn about PanHunter?
- We have prepared a series of training videos that covers most of the apps, their functionality, and how to use them. We also discuss some best practices within those videos.
How can I get additional PanHunter training?
- If you, or a member of your team, is new to PanHunter or would like to receive additional training (exceeding what is covered by the training videos), send an e-mail to panhunter_support@evotec.com and ask for a respective training session.
Where do I find more in-depth information about different apps?
- While working with PanHunter, you will see the help link at the upper-right corner of the page. This leads you to the documentation of PanHunter.
What do I do if I need help with specific analysis or explanation of feature in PanHunter?
- In case PanHunter Help documentation does not provide answer or solution to your issue, please use the Contact Support buttom or write an email to panhunter_support@evotec.com and our team will try our best to help you.